APRS

APRS [1, 2] is a Protocol for digital radio link. On the basis of this Protocol, built a global communication system. Its main objectives: transmission of information about the coordinates of objects in space, messaging, data transmission from the weather stations and much more.
What is this paper about? In General the APRS — is large, complex and confusing topic even for most hams. But habré Amateur radio not very much. So I would like to show that the standard is very good and can be used outside of Amateur radio. There are numerous systems where the exchange of messages on coordinates is invented again and again (transport), invented the transmission formats of information, e.g. from weather stations developed methods of sending text messages. However, if the creators of these systems knew about the standard APRS would be able not only to save time(at least on the development of a Protocol), but also to apply a number of ready-made software and hardware solutions.
Most of their knowledge about the system I got not practical using existing software and equipment, and develop their own programs and utilities to work with it [3, 4]. Information derived from the standard [5], Xastir source code[6], Amateur radio forums [7, 8] and of communicating with radio (all not count).
If you do:
the
-
the
- weather station; the
- system two-way text messaging via the Internet or radio in the form of a decentralized system using other pagers as repeaters; the
- satellite system; the
- monitoring telemetry remote stations; the
- on a hot air balloon;
Yes, and in almost every case when you want to build a system of data transmission via radio invent for this Protocol, then the hams have experience in various digital modes of communication and Protocol for APRS.
What is APRS?
In fact it is a standard that describes the types and formats of messages that can be transmitted over the network. The packet format may be slightly different depending on the transmission medium (see below), but the content and purpose of the package does not change.
Message types:
- Package from the weather station (WX) — contains information on meteorological conditions at a given point (temperature, pressure, humidity, force and wind direction). the
- Other message types.
lighthouse (Beacon) — perhaps the most frequently used message. It contains the Callsign of the station, its coordinates and a short comment.
a Short text message (Message) — an analogue SMS contains the Callsign of the recipient, sender and text short messages. the
Beacons and text messages is the most frequently used message types. There are still a number of message types, which can be found from the standard. Among them, for example, the message on the telemetry station that is to transmit freely definable parameters readings of some sensors.
How is the network and what parts?
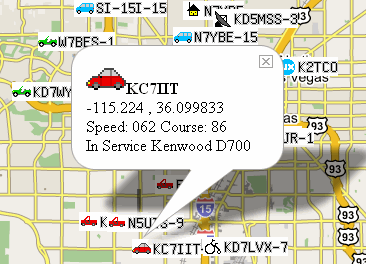 primarily, this station (mobile and stationary), there is still objects. In a network transmitted call sign (Callsign) and the coordinates (QTH) of a station or object. Further transmitted to the icon that identifies the purpose of the station (car, bus, house, etc.) and a short text comment. For example, I want to know where is now my car. Or worse — my wife wants to know where is my car! The network just performs the function of transmitting information on the station coordinates and other parameters to all interested parties. As a rule, the stations displayed on the map by the given coordinates. The other station, being a full participant in the network can send a text message to the other station. For example, the dispatcher taxi on the map to see a car that is closest to the desired location and sends a text message with the address where to go.
primarily, this station (mobile and stationary), there is still objects. In a network transmitted call sign (Callsign) and the coordinates (QTH) of a station or object. Further transmitted to the icon that identifies the purpose of the station (car, bus, house, etc.) and a short text comment. For example, I want to know where is now my car. Or worse — my wife wants to know where is my car! The network just performs the function of transmitting information on the station coordinates and other parameters to all interested parties. As a rule, the stations displayed on the map by the given coordinates. The other station, being a full participant in the network can send a text message to the other station. For example, the dispatcher taxi on the map to see a car that is closest to the desired location and sends a text message with the address where to go. Because in the ideal case, packets from the station have to get to the Internet. Then, anyone connected to the Internet can obtain information about the station. For this there are the global APRS servers. Thanks to the Internet, disparate parts of the radio network are combined into one global network of APRS (and the station can communicate with each other).
But as packets of information get on the Internet?
There is just so many options and huge scope for Amateur creativity!
The easiest option when a station has a direct connection to the Internet (for example, the program on the smartphone + GPS + mobile Internet, or the program on the stationary computer + Internet connection). This is a direct connection to the APRS server and the program is a direct receipt and dispatch of messages in the global network of APRS.
But it's boring! Hams also have their own radio broadcast!
Radio to transmit packets
It is believed that the APRS network has replaced packet radio. I believe that it is not so. Packet radio is Amateur radio version of the x Protocol.25, which is called AX.25[10]. Simple stack: physical layer transceivers send and receive the modulated signal, which is converted by the modems into bytes of information. The bytes are collected in bags. The packs contain everything you need: a source, a receiver (in the Amateur ax.25 this call sign), message, checksum. There are also methods of establishing and maintaining the connection acknowledgement(similar to TCP). There are packets without acknowledgment(similar to UDP). There used to be a large amount of BBS with whom you can establish connections via a radio broadcast, to receive and send mail. These BBS with the functions of mail communication on the Amateur radio satellites that could after some time, due to characteristics of the orbit, to fly over any place on the planet, transmitting mail anywhere.

Over time the Internet became available and shut down the needs of the message exchange. A network of packet radio stations began to decrease. But the remaining equipment. And this batch of equipment can be used now for the transmission of network packets via the APRS radio. That is, APRS is not replaced the packet, and packet communications rather only one type of packages package UI ax.25 (without delivery control) and the radio channel are used as the transmission medium of the communications network APRS.
Thus, packet radio is one of the ways of transmission of the APRS packet station in the system. In principle, can be used and other methods are used and types of modulations of the radio signal, such as BPSK, as a medium for transmitting messages to the APRS network.
And you need the Internet at all?
Everything seems to be fine, but suddenly the post-Apocalypse, sanctions, accident provider? Can the system work without the Internet? That part of the system that uses the Internet, of course, will fail in an accident. It will be impossible to know the coordinates of the objects through the browser and the station, directly connected to the global APRS will remain without communication. However, the part of the system that uses radio for communication, able to work independently.
A well-developed APRS radio network implies a network station class — radiodetermination (batch repeaters — digipeater (DIGI)). We can draw an analogy with base stations of cellular communication. These stations are high, hear far away, and receive signals from mobile stations moving objects, which typically operate at VHF. After receiving APRS messages it relays DIGI (that's a topic for another conversation, because the package modificeres, the path can be added to the DIGI Callsign in order to understand the path or the packet is discarded under certain conditions).
In addition to repeaters, there is another class of stations, bridges (GATE) they can forward a packet from one range to another. For example, if a GATE has two radios on different bands, it can transmit the packet from one range to another. The communication range of the VHF can reach 50km and GATE taking the packet on VHF can pass it on HF, where the package may be transferred for hundreds of miles. Thus, the package will "fly" to another city. And if there was a network that covered all the necessary areas using DIGI and would connect them with each other, then the Internet would not be needed. But such a decision has financial and technical limitations. Therefore, there is another class of plants — gates, which are connected to the Internet — IGATE. It is through them packets from a radio broadcast into the world's network of APRS.
How to operate APRS servers?
APRS world's servers connected to each other and exchange messages that each of them makes. The clients of these servers is a terminal station, which are connected to the Internet directly APRS messaging or IGATE stations that send packets from the airwaves to the worldwide web. Other stations, whatever server they were not connected, you get this message. Messages in the global network very much, so servers support the filtration system according to certain parameters.
Network APRS network real time!
The packet from the station on the radio, in the void, with no guarantee of delivery. But if the package is accepted, it will be immediately processed/relayed/sent on, or the Internet. The received packet will be immediately displayed on the world map, if you have the appropriate software. In object properties you can view on how much outdated data from the object. Despite the lack of guarantee of delivery, a mechanism for the confirmation text message (we send the message N times until you get an acknowledgment from the addressee).
List of used terms and abbreviations
the
-
the
- SQ — short wave the
- USW — ultra short wave the
- Internet APRS Server server in the Internet through which you can exchange messages, receive and send APRS packets, for which there is an accumulation of data. As a rule, all the world's APRS server is connected and the message received from IGATE on one of the servers gets on all the other servers. the
- CALL — call sign of the station the
- Digipeater (DIGI) repeater packages the
- GPS device that allows you to determine your exact coordinates the
- GATE — bridge for transmitting APRS packets to other ranges the
- IGATE — the bridge to transmit APRS packets on to APRS Internet Server the
- the SID is a number from 0 to 15, appended to the Callsign of the station (e.g. UA3MQJ-4). Used to identify multiple stations under one call sign. The same SID in standard APRS, you can determine the purpose and type of station (mobile station, GATE, etc.). If SID is not specified, it is considered that it is equal to zero. the
- Transceiver — transceiver. Typically, designs use a common schema parts for the transmission and reception of the signal. the
- TNC controller for controlling the operation of the modem and transmitter connected to the computer KISS TNC — TNC supports KISS mode the
- Modem — device for modulation/demodulation of a signal according to a specific Protocol (e.g. Packet) the
- Package APRS — packet information corresponding to the Protocol APRS (beacon message, etc.), regardless of the transport Protocol transmission. the
- Package AX.25 — pack information corresponding to the packet communication Protocol AX.25 the
- Transport Protocol and medium used to transmit APRS packets (such as packet AX.25 can be transferred via radio or via network tcp/ip or in text form to the Internet APRS server)
Examples of devices and solutions to work with APRS
1 Stationary PC with Internet connection, no radio, no GPS
Equipment:
the
-
the
- desktop computer. the
- Connection to the Internet (GPRS/ADSL/etc).
Software:
the
-
the
- Client APRS — UI-View
Capabilities, we get:
the
-
the
- maps and stations on maps. the
- View parameters of stations (for moving, for example, the speed; for weather stations — weather settings, etc.). the
- Receiving and sending text messages. the
- sending a beacon with information about their station with fixed coordinates.
Review: this is probably the easiest option that can be.
1.1 Portable PC with connection to Internet, no radio, c GPS
Equipment:
the
-
the
- (M) laptop. the
- (+) a Connected GPS receiver.
Review: in this configuration, your coordinates will automatically change over time and other members of the APRS network will be able to see your movement.
1.2 PC laptop without connecting to the Internet, transceiver, c GPS
Equipment:
the
-
the
- (M) laptop. the
- (+) a Connected GPS receiver. the
- (+) Connected to the transceiver.
Review: in this configuration, your coordinates will automatically change over time and this information will be transmitted on the radio. If your packages will be accepted via the radio to other members of the network APRS, they will be able to see this information. If the packets are accepted by the station connected to the global APRS network (IGATE), that information will be able to see everything.

1.3 Stationary PC with Internet connection with transceiver
Equipment:
the
-
the
- (+) Connected to the transceiver.
Review: in this configuration, the station can receive, send and process packets as the global network of APRS and radio, within its area of coverage. Such a station can operate as IGATE (send received packets from a radio broadcast in the global network of APRS).
1.4 a Stationary PC without Internet connection, with transceiver
Equipment:
the
-
the
- (+) Connected to the transceiver. the
- (-) is Missing.
Review: in this configuration, the station can receive, send and process packets from the radio, within its area of coverage. Such station can be operated as a DIGI (to relay packets received from the radio). If within radio visibility of this station is IGATE, the packages can get into the world network of APRS (for example, you can use the service to send text message by EMAIL to the Internet, while in some deep forest or in the sea).
1.4 Stationary PC with Internet connection with receiver
Equipment:
the
-
the
- (+) the receiver is Connected.
Review: in this configuration, the station can operate as IGATE, performing this important function. If you try, you can do not even an Amateur receiver, and a USB dongle with SDR technology and properly interconnect all programs.
Remark how to connect the transceiver to the station APRS
Generally, transceivers are designed to transmit the human voice. The digital signal is transmitted in the same frequency band as the speech (as in modems in telephony). To transmit and receive modulated audio frequency digital signal, the transceiver may have a separate line input and output (they do not make changes to the signal).
But the signal must be modulated and demodulates. With respect to packet communication to operate on HF is used AFSK 300 baud. Frequency modulation: one frequency is "1", the second frequency is "0". Initially, the work was used modem. At the reception he distinguishes 0 from 1 with filters, transfer switch, two frequency generator. The resulting stream consisting of zeros and ones is converted into packets using a special device — TNC (batch controller). Thus, the connection scheme was as follows:
the
RS232 RX,TX(TTL) RX,TX(Audio)
PC <-------> TNC <----------> Modem <-------> Transceiver <------> Antenna (and ether)
Over time, parts of the chains become aligned in one device. For example, there are transceivers with built-in modem; have a TNC with a built-in modem; I think there are even ready-made blocks, TNC to the transceiver. Very popular is the decision on the basis of the program MixW. In this case, the TNC and the modem is emulated by the program MixW, and the transceiver connects to a computer's sound card. From the APRS FOR this program acts as KISS TNCи the interaction occurs via the COM port. By the way, two COM ports and a null modem cable is not required. In the present set of tools MixW virtual driver null modem where you can set pairs of connected virtual serial ports. The program APRS will be considered that interact via a hardware COM port with hardware TNC. Overall, the program is MixW, a very developed, there is even a driver for the network adapter, which will transmit data using packet radio(tested on Windows). You can connect two computer through the sound card and opengovdata. But all, of course, on the radio.
There are transceivers designed specifically for working in a network of APRS, who independently perform a particular functionality.
Examples of devices and solutions to work with APRS (second series)
2 Smartphone
Equipment:
the
-
the
- Smartphone.
Software:
the
-
the
- Client APRS — APRSdroid
Review: in this configuration, the station is always in his pocket, and the map can be displayed as people (and not cars).
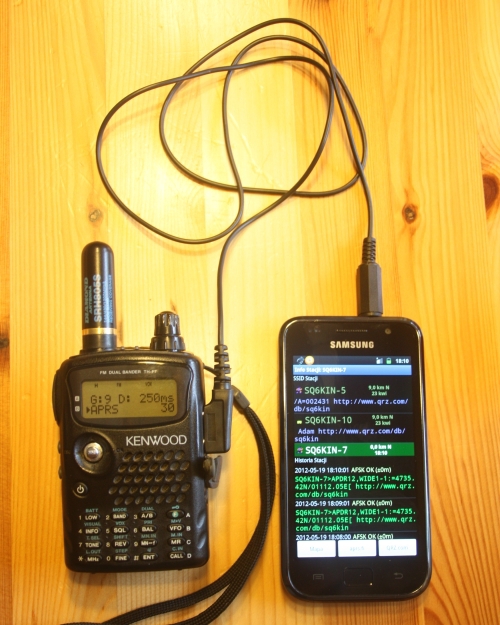
2.1 Smartphone + transceiver
In fact, I don't know the details, but the photo speaks for itself.

3 APRS tracker
Yes, Yes, that's exactly what sold under the name "satellite alarm". Tracker — automatic device, which is either just writes the coordinates and time or plus can transmit beacons on the air. User interaction in the process is not assumed. Put trackers in cars, balloon launch.
www.byonics.com/tinytrak

4 the Router connected to the Internet
If the goal is simply to mark on the map of the world his station at fixed coordinates, a clock drive for this personal computer is not very convenient. First, not every computer runs around the clock; secondly, you can forget to run the program; third program will hang in the tray; fourth, after each reinstallation of the windows all need to re-configure. And in General, drive PC for the sake of sending one package — too "bold". For such purpose the best is a simple device, working 24/7, with low energy consumption. The router — the most suitable option.
On the router installed firmware OpenWRT, you can run the client APRX and you will always be on the map. I did one on your router TP-Link TL-MR3020.
5 PDA with Windows Mobile
There is a client for PDA — APRS/CE.

How to get into the APRS network?
Any radio Amateur with the Callsign can connect to the Amateur radio APRS network and use this network to Amateur radio purposes. If you are a radio Amateur and don't want them to become, or you want to use technology to build their networks and in their personal, or commercial purposes, then you will need to adjust some points.
How to raise your APRS server for your system? Is it possible to use a radio if there is no Amateur radio call sign? What you can use the transceivers, and how to connect to it? All this, and many other technical issues (e.g. message formats, the range at radio frequencies, modulation types) — that's a lot for one article, and besides, I'm tired too :) If the topic is interesting, we shall proceed with it.
in the meantime, all best wishes 73 de UA3MQJ!
references
1. http://aprs.qrz.ru/ Website APRS Russia.
2. https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/APRS information on Wikipedia
3. https://code.google.com/p/qaprs/ is my experimental project QAPRS (Qt4) for desktop PCs.
4. https://code.google.com/p/japrs/ is my experimental project jAPRS (JAVA ME) for mobile phone without GPS.
5. http://www.aprs.org/doc/APRS101.PDF — PDF file — standard APRS.
6. http://xastir.org/
7. http://forum.qrz.ru/27-aprs.html — APRS thread in the forums QRZ.RU
8. APRS thread in the forums CQHAM.RU
10. description of the Protocol is AX.25 (PDF)
11. http://www.qslnet.de/member/rz3tw/ap_st/ap_st.htm — APRS — what is it?
12. http://www.mixw.net/index_rus.php website software to work digital modes MixW.
13. APRSdroid — APRS for Android
14. www.byonics.com/tinytrak
15. Client for Windows mobile
16. http://hamcmw.qrz.ru/pr/index.html — Amateur radio packet communication (Packet Radio) and APRS
Important: the technology of APRS is given in the article for informational purposes only. It was developed by Amateur radio operators, to identify the stations used for Amateur radio call signs, the global network of APRS — is Amateur radio servers and radio frequency at which communication occurs, is used on the basis of permits issued. You are prohibited from using Amateur radio servers and radio frequency band, if you are a radio Amateur. However, the technology and message format can be used in your projects, using your servers. You can even use the radio, if you bought the frequency or using frequency bands, power and types of modulation, which allowed the scrd to use without any registration.
Комментарии
Отправить комментарий